3 port C+L Band Polarization Insensitive Optical Circulator
Description
GEZHI’s polarization insensitive optical circulator utilizes proprietary designs and metal bonding micro optics packaging. It provides low insertion loss, broad band high isolation, low PDL, excellent temperature stability and optical path epoxy free. It can be used for wavelength add/drop, dispersion compensation and EDFA application.
Features
♦ Low Insertion Loss
♦ Wide Band High Isolation
♦ Low PDL
♦ Compact In-Line Package
♦ High Stability and Reliability
♦ Epoxy-free on Optical Path
Applications ♦ Optical Amplifier
♦ Wavelength Add/Drop
♦ Dispersion Compensation
♦ Bi-Direcation Communication
Technical Paremeter
Parameter | P Grade | |
Configuration | Port 1 to Port 2 to Port 3 | |
Operation Wavelength (nm) | 1525 to 1610 | |
Isolation (dB) | Typical | 0.8 |
Maximum | 1.0 | |
Typical Isolation (dB) | 50 | |
Minimum Isolation (dB) | 35 | |
Cross Talk (dB) | ≥50 | |
Polarization Dependent Loss (dB) | <0.2 | |
Polarization Mode Dispersion | <0.1 | |
Return Loss(dB) | ≥50 | |
Power Handling (mW) | 500 | |
Opterating Temperature (℃) | -5~+75 | |
Storage Temperature (℃) | -40~+85 | |
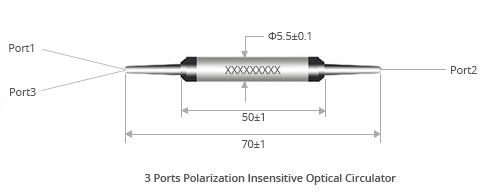
Package dimension (mm) | Φ5.5xL50 orΦ5.5xL63 | |
Specifications may change without notice.
Above specification are for device without connector.
Ordering Information
IC | X | XX | X | X | X | XX |
Port | Wavlength | Grade | Fiber Type | Fiber Length | In/Out Connector | |
3=3 Port | CL=C+L Band 1525~1610nm | P=P Grade | 1=Bare fiber 2=900um loose tube | 1=1m
| 0=None 1=FC/APC 2=FC/PC 3=SC/APC 4=SC/PC 5=ST 6=LC S=Specify |
Application Diagram
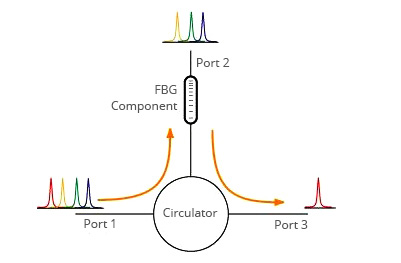
As the picture shows: The input DWDM channels are coupled into Port 1 of the device with a FBG device connected to Port 2. The single wavelength reflected from the FBG then reenters the Circulator in Port 2 and is routed accordingly to Port 3. The remaining signals pass through the FBG and exit on the top fiber.
Circulator used to drop an optical channel from a DWDM system using a Fiber Bragg Grating.
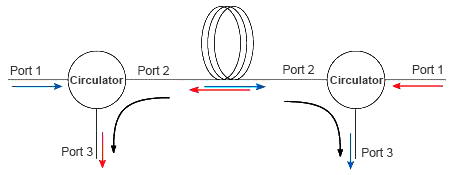
As the picture shows: A Circulator is located at both ends of the fiber. Each Circulator functions to add a signal in one direction while removing the signal in the other. See the example to the left.
Circulator can be used to send optical signals through a single fiber in two directions.
Dimension